Tact Hello World
Tact contract structure
Tact's facts #3
Contracts and Messages
A lot of important details you should learn to understand how TON works, but here, we simplify our field of knowledge and goals. So, let's say, contracts and messages are our main characters in blockchain.
-
Contract - is a computer program that lives on the blockchain. It can store information and carry out certain actions based on the instructions that are written inside it.
-
Message - is a command that we send to the contract. It tells the contract what to do and can include information like how much funds to transfer or what information to deliver.
On the scheme, you can see a representation of how blockchain works, where different contracts communicate with each other by messages.
Get functions
Additional general tool, that extends functions of the contract - is getter or get function. This feature allows to get read-only information from contract's data. Usually, get-function is using to deliver information(for example, smart-contract current balance) to the application, but it is impossible to call it from another contract.
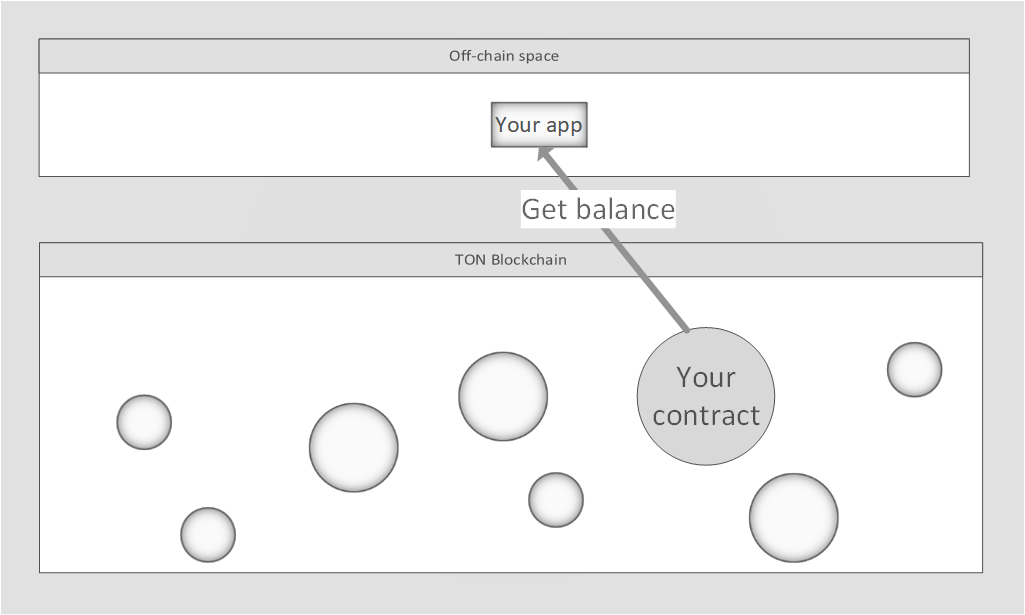
Read more about contract structure here.
Smart contract development
In summary, the main goal of smart contract developers is to declare and write the logic of actions in a smart contract correspondingly to messages it gets from other smart contracts. If it is necessary to get information and deliver it off-chain(common web app), there are get functions that should be declared.
Let's talk about the design of our contract. Our smart contract is like a piggy bank with several common features:
- Keep Total value. We will keep
Totalinteger value in blockchain. - Get Total value. Special tool for reading current
Totalvalue from blockchain. We can read this directly from blockchain via specialgetmethod. - Processing "Increment" text comment command. When contract gets a message, it checks what the message says. If the message says "Increment," it will add
1to theTotalinside the piggy bank and update it. - Processing
Addmessage command. If the message says "Add," it will add a specific number to the Total inside the piggy bank and update it.
Additional restriction for our smart contract - It will check if the person sending the message is the owner of the piggy bank or not. This way, only the owner can add or increment the Total inside the piggy bank.
Tactical practice #3
Import modules
Come back to tact-guide-template project via IDE(VS Code) and begin to write the contract file contract.tact. That, our first Tact string is declaring an additional library, where some useful Tact functions are defined.
import "@stdlib/deploy";@stdlib/deploy module extends our tools with Trait Deployable, so we can use it Trait later for implementing contract's deployment feature easier.
Note, that Tact language consists of some unusual for classic program language entities, here is what we face in this guide:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Contract | Tact type that declares contract entity in it's {} block. |
| Message | Tact type for convenient message's declaration. |
| Trait | Struct similar to Contract, but serves as extension for Contract(it's similar to interfaces or inheritance for Classes in classic Object‑oriented PL). |
| Address | Smart contract address in according TON standards. You'll see this parameter as sender or destination of messages. |
Read more on the Tact type system page.
Define Structure
Next step, we need to specify our message Add, that will force contract do actions according to 4th feature.
Here we specified, that our message should content Integer number of 32-bit length.
//previous code
message Add{
amount: Int as uint32;
}Contract body and fields
Now we begin declare our contract, we will call it SampleTactContract. Also, we need specify our contract's own properties, that will be stored in its storage: owner and counter.
//previous code
contract SampleTactContract with Deployable {
owner: Address;
counter: Int as uint32;
As said before Address defined in the Tact Type system that describes smart-contract's language. General information about Address in TON placed here.
owner- is Address of owner set in forSampleTactContract, and we will use it for double check if message sent by owner or not.counter- integer number stored in contract that keep current value of iteration results.
Writing Init function
Before we can use contract in Blockchain we should define its initial process. In our case, it means, that we should declare contract's function, that will define our owner and counter in particular.
This tool in smart contracts called init() function, and we need describe its behaviour next:
//previous code
init(owner: Address) {
self.owner = owner;
self.counter = 0;
}Where self - special Tact keyword of current level struct, here we using it for contract's fields we declared. Function init() will:
- Accept one argument of type
Address, set this in contract's fieldowner. - Initialize
countervalue equal to 0.
//previous code
contract SampleTactContract with Deployable {
owner: Address;
counter: Int as uint32;
init(owner: Address) {
self.owner = owner;
self.counter = 0;
}
// recievers definition here
// get functions definition hereWe defined basic structure of our contract. Next step is adding receivers and get functions.